2 5 Factorial Design. The 2k Factorial Design Montgomery chap 6. BHH 2nd ed chap 5 Special case of the general factorial design. For example if your experiment is extremely costly you might be able to run the base design only one time. Im gathering the data through simulations so I.
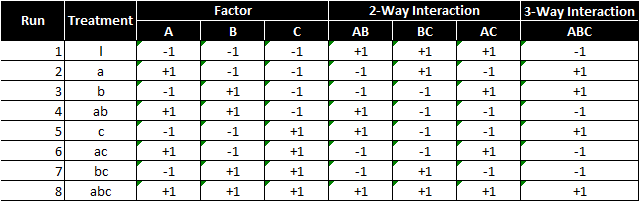
Factorial experiments can involve factors with different numbers of levels. Discuss 22 factorial designs with relevant example. Column I the identity vector is not considered for 1 2 1Sum of each column in the sign table is 0 sumSj 0 for all j 1 2Sum of the product of any two columns is 0 sumSj Sk 0 for all j k 1 j k 3Sum of the square of elements in any column is 2k-p sumSj Sj 2k-p for all j. 62 - Estimated Effects and the Sum of Squares from the Contrasts. If equal sample sizes are taken for each of the possible factor combinations then the design is a balanced two-factor factorial design. Factorial design is now twice that of OFAT for equivalent power.
To get the correct design calculate the number of factors in the base design by subtracting the number of design generators from the total number of factors that you want.
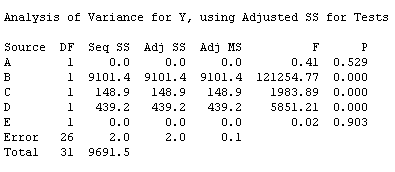
5 2k-p Design Properties Note. I have a 25 factorial design so I have 32 runs of my experiment with the appropriate - values outlining the 32 possible combinations. 5 Two-Level Fractional Factorial Designs Because the number of runs in a 2k factorial design increases rapidly as the number of factors increases it is often impossible to run the full factorial design given available resources. Factorial design offers two additional advantages over OFAT. 72 - The 23 Design. Namely Pressure factor X 1 Table speed factor X 2 and Down force factor X 3 each at a high and low setting on a production tool to determine which had the greatest effect on product uniformity.