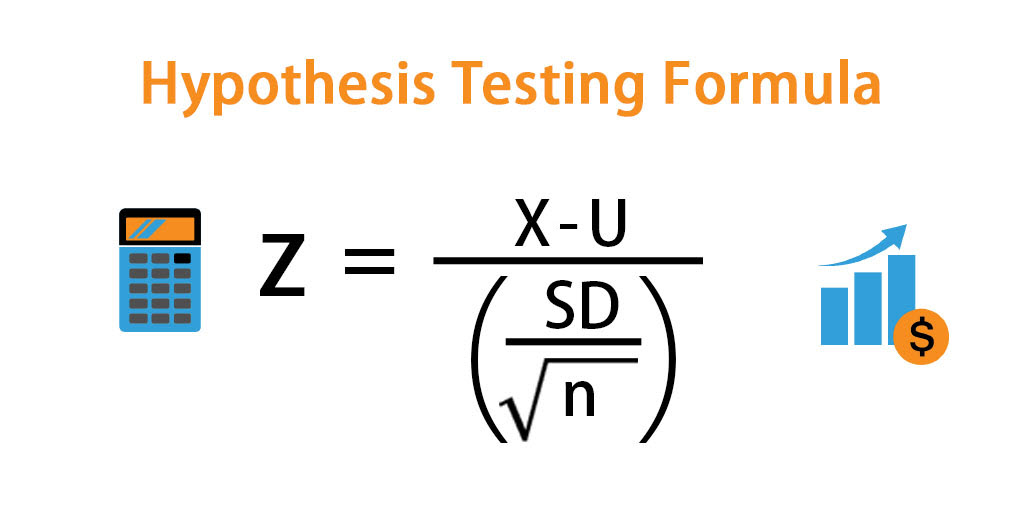
2 Sample Z Test Formula. WHY WE USE LARGE SAMPLE. Compute the test statistic. Define Null and Alternative Hypotheses. Z-test is a statistical method to determine whether the distribution of the test statistics can be approximated by a normal distribution.
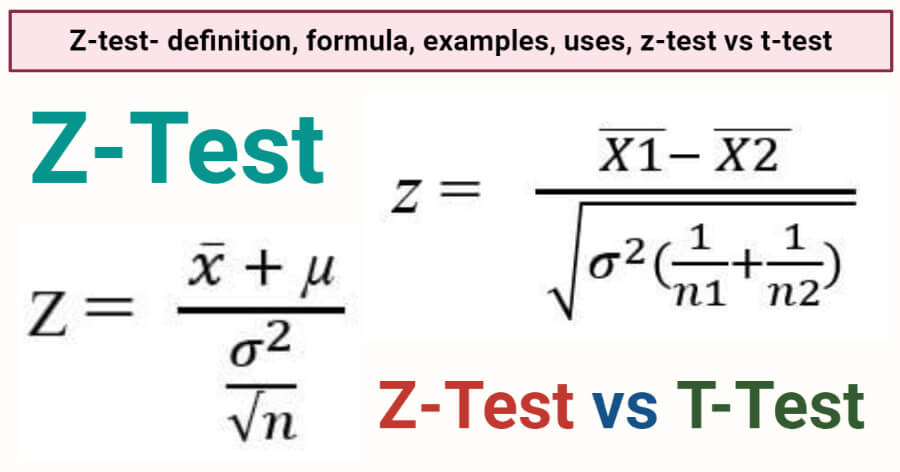
Z Test in statistics refers to the hypothesis test which is used to determine whether the two samples means calculated are different in case the standard deviations are available and the sample is large. Z-test is a statistical method to determine whether the distribution of the test statistics can be approximated by a normal distribution. Let μ1 average number of plates produced by machine1 per minute. Lets take an example to understand the usage of two sample Z Test. Two Sample Z Test. While using the Z Test we test a null hypothesis that states that the two populations mean is equal.
Compute the test statistic.
Decisionwhether to accept the null hypothesis Ho and reject alternative hypothesis Ha or vice versa Step 5. Z x 2 x 1 2 1 SE di 102 122 0463 4320 3. Decisionwhether to accept the null hypothesis Ho and reject alternative hypothesis Ha or vice versa Step 5. Z p 1-p 2 p1-p1n 1 1n 2 where p 1 and p 2 are the sample proportions n 1 and n 2 are the sample sizes and where p is the total pooled proportion calculated as. While using the Z Test we test a null hypothesis that states that the two populations mean is equal. State the null and alternative hypotheses.