
Kruskal Wallis Test Formula. Definition Formula and Example. P-value 1 CDF χ 2H df P-value 1 CDF χ 2H adj df For small samples Minitab recommends that you use exact tables. This is an independent-measures design so you need two columns. To conduct the Kruskal-Wallis test using the K independent samples procedure cases must have scores on an independent or grouping variable and on a dependent variable.
KRUSKALR1 ties value of H on the data without headings contained in range R1 organized by columns. The first 60 records rows are the same as the. Ch 05 Example 01 ANOVA and Kruskal-Wallis Testsav. A dataframe containing the variables in the formula. A Kruskal-Wallis test is used to determine whether or not there is a statistically significant difference between the medians of three or more independent groups. The Kruskal-Wallis test is similar to Wilcoxons Rank Sum test in that we are comparing the sum of ranks applied to the data.
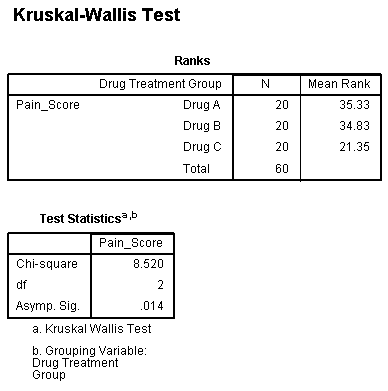
A Kruskal-Wallis test is used to determine whether or not there is a statistically significant difference between the medians of three or more independent groups.
These assembled measures are rank-ordered from lowest rank1 to highest rankN with tied ranks included where appropriate. Test example data set used in Chapter 4 records 61 through 90 are new for Group 3. The formula for the Kruskal-Wallis test is H frac12NN1left fracR_12n_1fracR_22n_2 cdots fracR_k2n_kright - 3N1 where N is the total sample sizes the sum of the sample sizes and R_i is the sum of ranks for sample i from a. Enter the data into SPSS. These assembled measures are rank-ordered from lowest rank1 to highest rankN with tied ranks included where appropriate. Notice that this data set has 90 records.